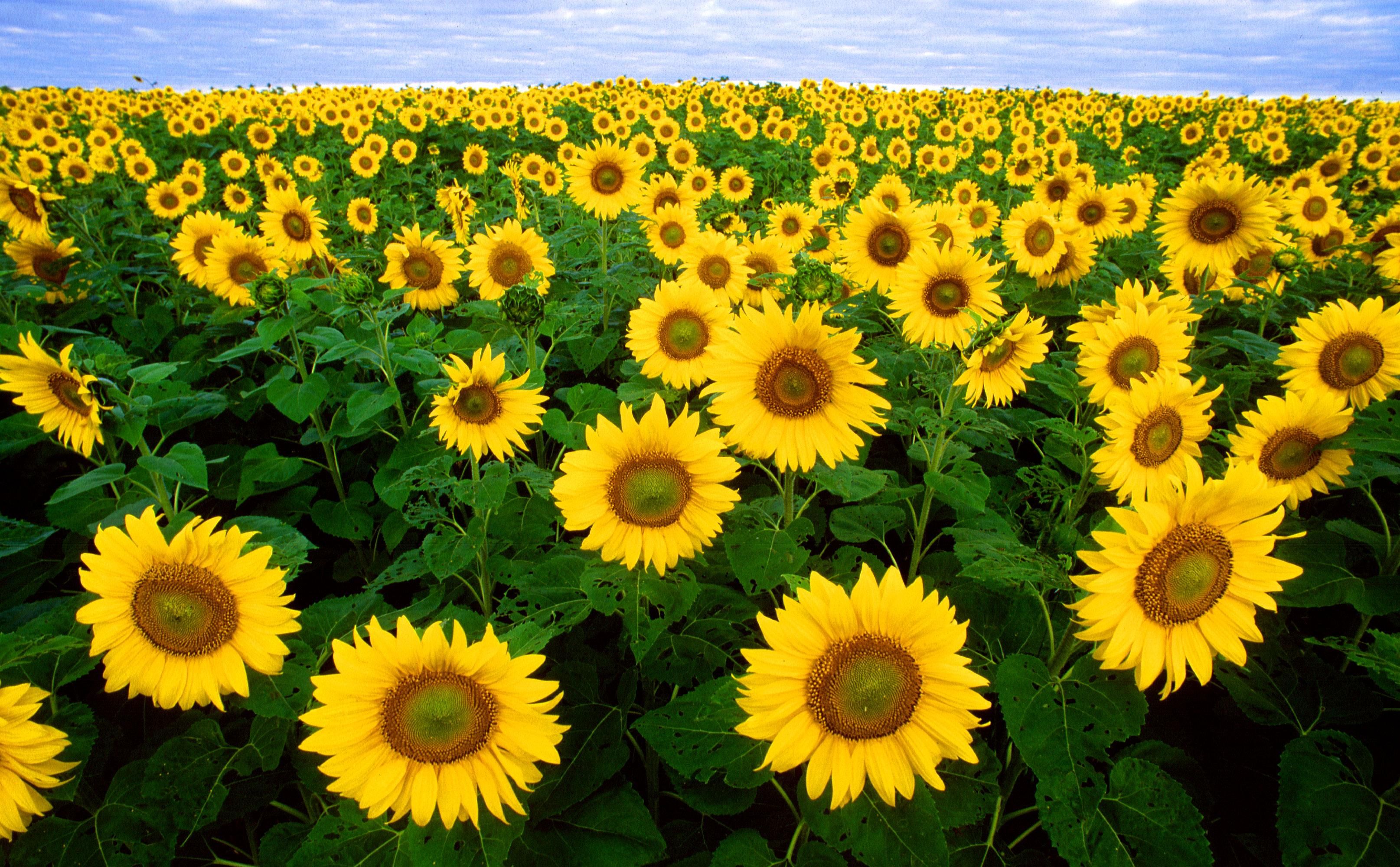

Credit: Bruce Fritz, U.S. Department of Agriculture, public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
You might think that plants are stationary, but did you know they can dance?
Many flowers do a daily sun dance, swinging from east to west, to produce more pollen and attract insect pollinators.
They make this movement using two methods:
Plants contain a compound called phototropin that responds to being in shadow by causing cells to elongate. In this way, the dark side of the plant grows longer, which curves the other slower-growing side toward the light.
All plants do this, but the sunflower is special. It can elongate its cells every minute!
Each day as the Sun moves westward, cells on the east side of the stem just beneath the flower grow, tilting the flowerhead westward to follow the Sun. At night, the west side grows, pushing the flower back toward the east to greet the morning sun.
The sunflower will do this daily dance until fully mature, when it stops growing, usually with the head facing east.
Other plants in the sunflower family, like daisies and dandelions, can also follow the Sun, but use a different method. They pump potassium and water across cell membranes to inflate or deflate cells, thereby bending the stem.
Using these methods, many plants can change their orientation, not only to light, but moisture, gravity and other stimuli.
Not exactly dancing, but moving in rhythm more than we might think.
Background
Synopsis: Plants are rooted in place, but they still move in response to external stimuli. Most plants grow toward light, but some actually follow the Sun on a daily basis, tracking from east to west, then resetting back to east-facing during the night to be ready for the rising Sun. Heliotropic flowers, like sunflowers, daisies and arctic poppies, have different mechanisms for tracking the Sun. They have inspired materials scientists to create “sunbots,” tiny solar robots that also track the Sun.
- You might think of plants as static organisms because they are rooted in the ground, but plants are able to shift their orientations in response to light, gravity, moisture and other external stimuli.
- When plants grow toward a strong light source, they elongate the cells farthest from the light to cause their stems to curve.
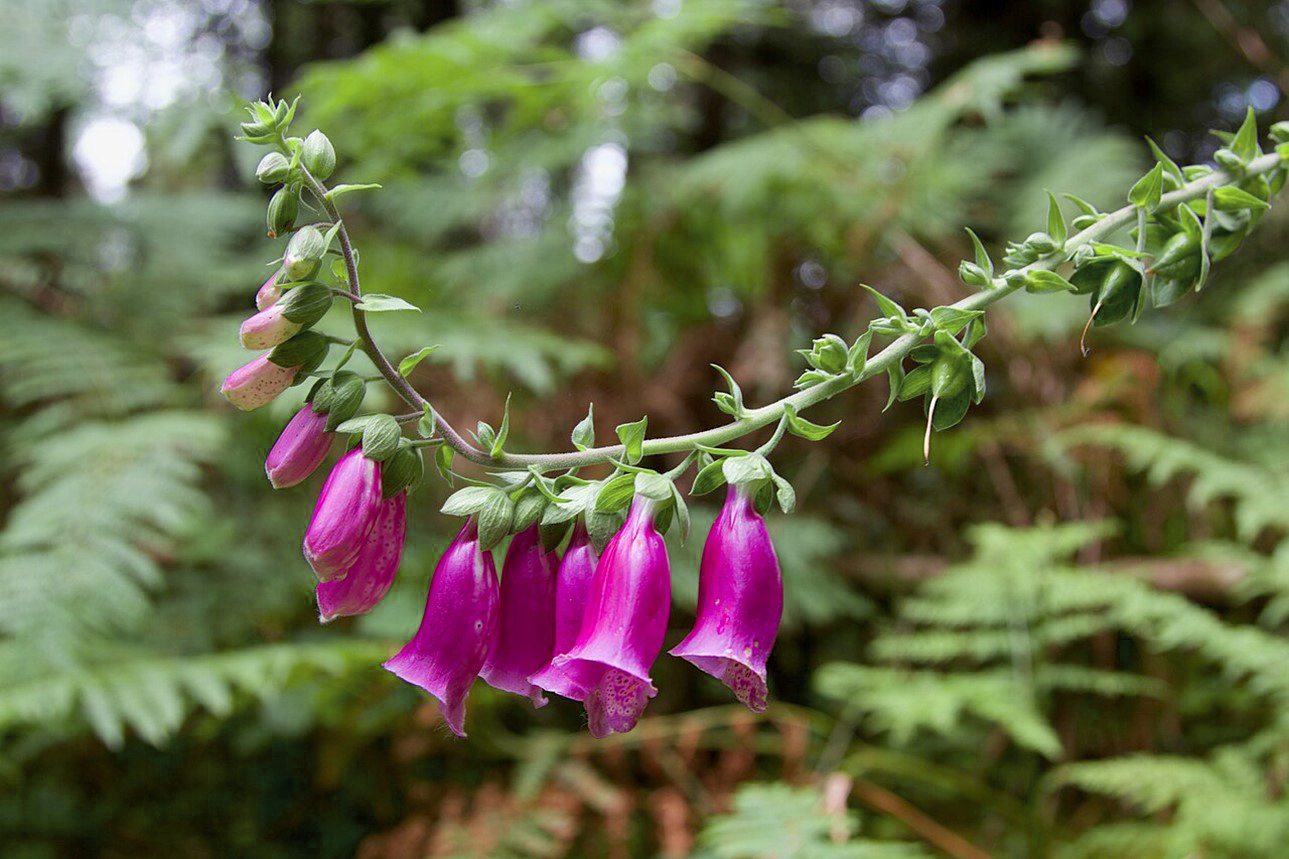

A curved stem of foxglove flowers grows toward the light.
Credit: Randusr836, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons - This irreversible curving differential growth is known as phototropism, which is governed by a molecule called phototropin, which responds to light at the blue end of the electromagnetic spectrum by activating plant hormones called auxins in the plant stem.
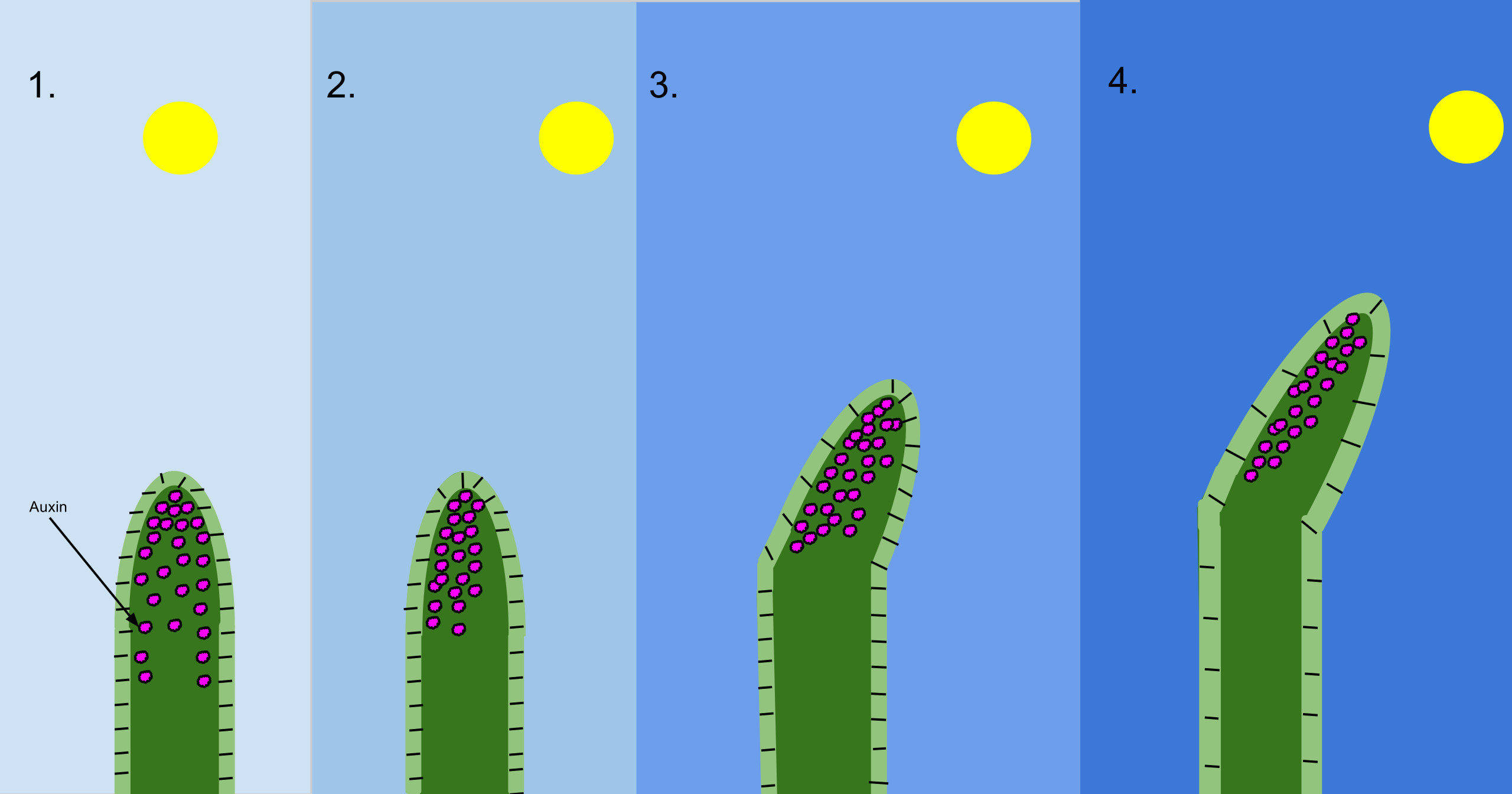
1. This is a normal plant that has the Sun positioned almost directly overhead. During this time, the auxin (pink dots) within the plant is evenly distributed. 2. The Sun is now positioned at an angle to the plant. The repositioning of the Sun causes the auxin to concentrate on the far side of the stem. This overload of auxin causes nearby cells to elongate. 3–4. This causes the stem to bend irreversibly toward the Sun.
Credit: MacKhayman, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
- When plants grow toward a strong light source, they elongate the cells farthest from the light to cause their stems to curve.
- Some plants are heliotropic, invoking a dynamic, oscillatory type of phototropism that enables the plant to continuously turn specific surfaces toward the Sun to maximize direct solar radiation, returning them to their starting position overnight.
- Heliotropic plants move to readjust to prevailing light conditions about every 15 to 60 seconds.
- For flowers, tracking the Sun warms flower surfaces to optimize pollen development and attract insect pollinators. This can be especially important for high-latitude flowering plants because of their short growing season.
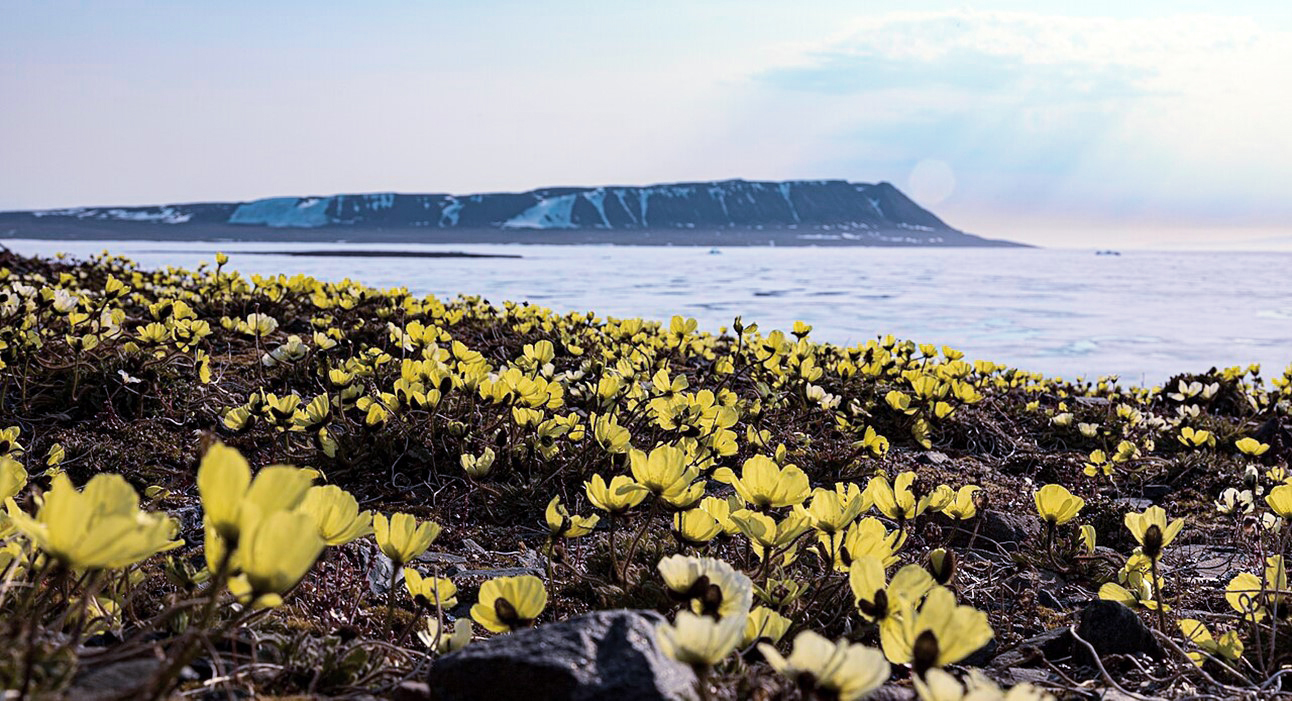

Arctic poppies on the shore of Russia’s Proliv Shokal'skogo (Shokalsky Strait) at 78.5°N latitude. These high arctic bloomers have cup-shaped flowers that move with the Sun, focusing sunlight on the center of the flower. With only 50 to 60 days of growing season, amplifying the Sun’s warmth enables the poppies to grow faster and attract insects for pollination.
Credit: Nestortech45, CC BY 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons - For leaves, heliotropism enhances light interception for photosynthesis.
- Many flowering species are heliotropes, including alfalfa, soybean and many members of the Asteraceae family like daisies, dandelions, poppies, buttercups and tulips.
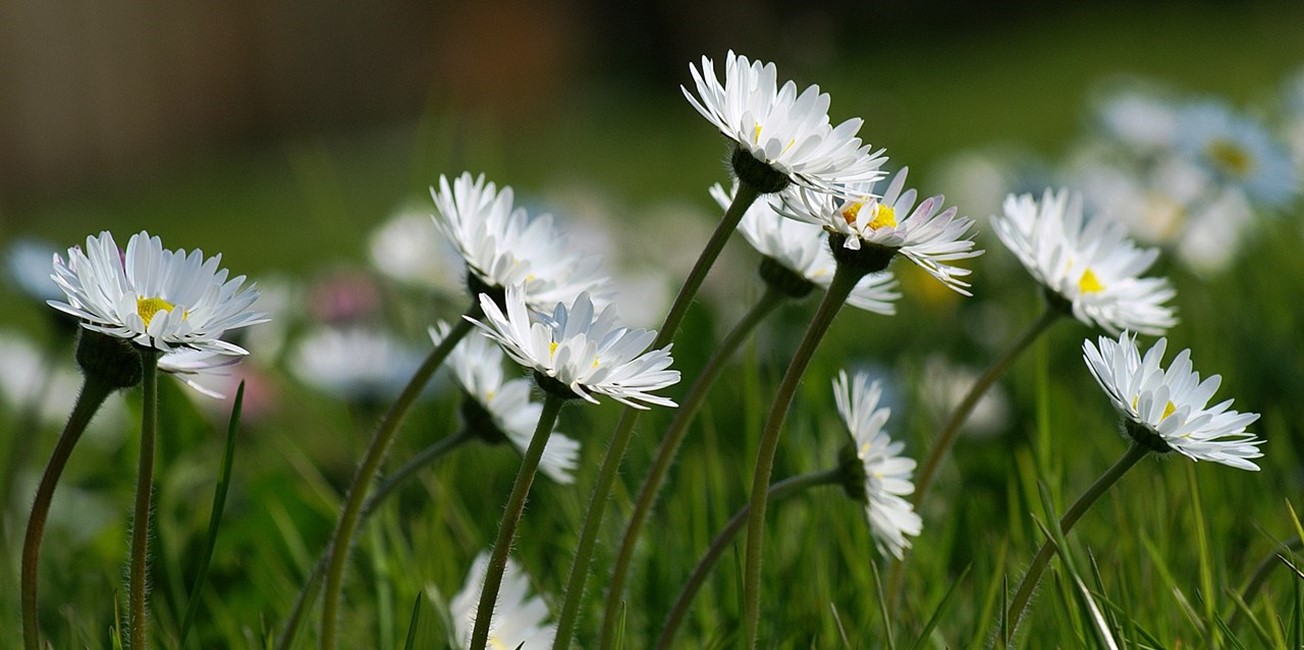

Daisies (Bellis perennis) face the Sun after opening in the morning and will follow the Sun through the day.
Credit: böhringer friedrich, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons - For many flowering heliotropic species, a special layer of cells called the pulvinus, just under the flower head, moves the flower head by pumping potassium and water across cell membranes to inflate or deflate cells in response to light.
- The same potassium-driven mechanism also operates in response to different types of stimuli. For example, it causes pores called stomates to close in response to water loss or mimosa leaves and flytraps to move in response to touch.
- Sunflowers are the most popular “poster child” for heliotropism, but they use a completely different mechanism than most other flowers to achieve their beautifully coordinated sun dance each day.
- In 2016, researchers discovered that while sunflowers and daisies both track the Sun and come from the same flower family, sunflowers accomplish their movement differently than most of their cousins in the Asteraceae family.
- Asteraceae flowers develop a flower head composed of hundreds or thousands of individual florets with varied purposes. Florets in the center become pollinated to produce seeds, while florets around the edge look like petals to attract pollinators but do not produce seeds.
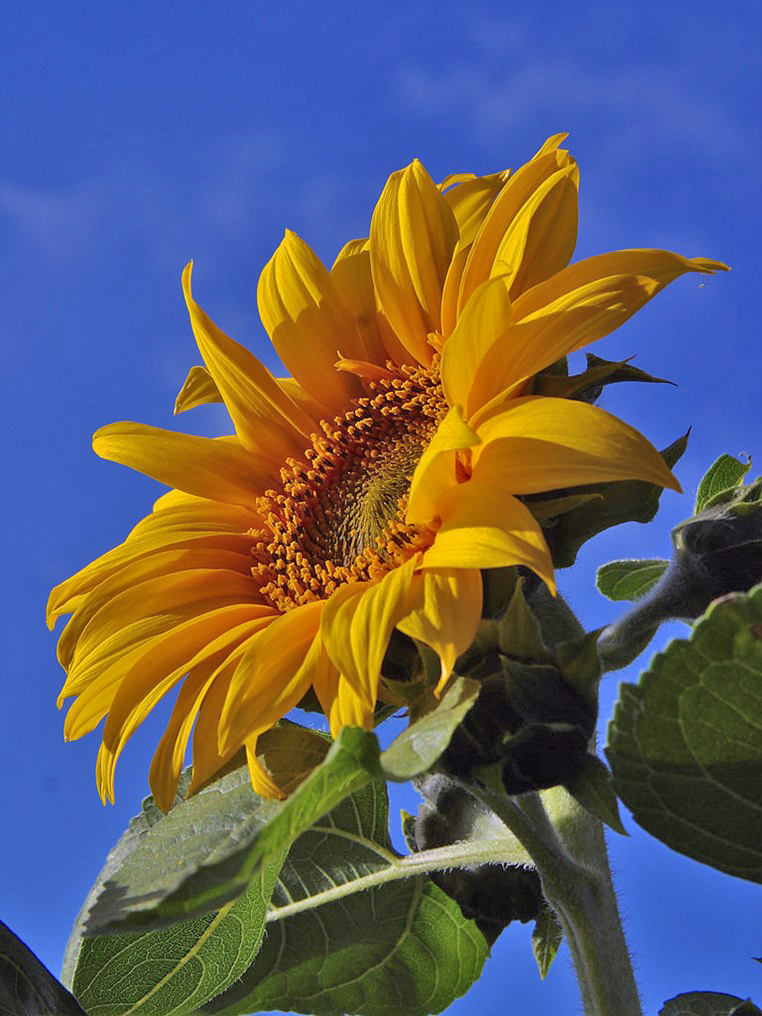

A sunflower (Helianthus annuus) in full bloom on a sunny day.
Credit: Jon Sullivan, public domain, via Wikimedia Commons - Young sunflowers track the Sun by varying the growth rates on either side of a flowering stem based on their internal circadian clock.
- They rely on multiple natural light sources, not solely the blue light that drives phototropism.
- As the Sun arcs westward during the day, cells on the east side of the plant progressively elongate to push the head toward the west. Then at night, cells on the west side grow longer to push the heads back to their morning position, facing east to greet the dawn’s light as well as its warmth, which attracts pollinating insects.
- Every morning the process begins again, repeating until the sunflower is fully grown and its movement ceases as its stem stiffens, usually with the final orientation of flower head facing east.
- This final flower head orientation affects both flower development and reproductive success.
- East-facing plants warm up and release pollen earlier in the day, providing an energy benefit to foraging bees that are most active in the morning.
- Direct sunlight illuminates the ultraviolet markings that attract bees.
- East-facing flower heads also tend to produce larger and heavier seeds.
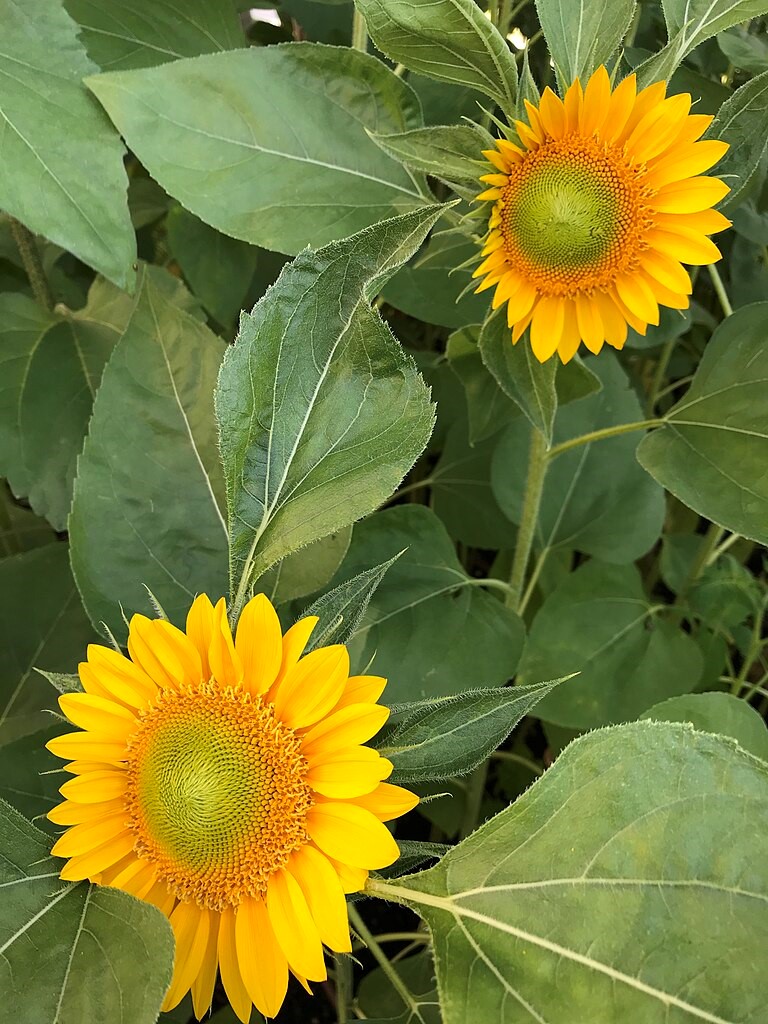

Young sunflowers track the Sun each day until they reach their mature height and stop growing with their flower heads facing east as their stems stiffen. Look closely at the photo and you will see that each of the individual florets are oriented at the “golden angle” of 137.5° relative to the next floret, producing interconnecting spirals. The number of left spirals and right spirals are successive Fibonacci numbers. This pattern produces the most mathematically efficient packing of seeds in the flower head.
Credit: M2545, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons

